Your mouth is your body’s finest organ. It’s used to eat, talk, and smile. Your mouth, just like the rest of your body, can be overcome by killing disease too. One of them is oral cancer. Oral cancer develops in your mouth and, when developed as much as to be found, can be transmitted to the rest of your body.
Oral cancer is risky because it may appear like a small sore or a small issue at first. Most people do not experience symptoms of the first stage because it is not an impending issue. Early detection is highly advantageous. The earlier it is detected, the easier to get better.
Here we are proceeding step by step to discuss the causes of oral cancer, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. After you have read this, you’ll be very well aware of what to look for and when to visit the doctor.
What Is Oral Cancer

Oral cancer is cancer in any of the parts of the mouth. This can be:
- Lips
- Tongue
- Gums
- Inner lining of cheeks
- Roof of the mouth (palate)
- Floor of the mouth below the tongue
Oral cavity cancer is also grouped with throat, tonsil, or base of the tongue cancer sometimes. Both are head and neck cancers.
Early Oral Cancer Signs
The issue with oral cancer is that early signs are extremely subtle and painless. You might not even notice they occur unless you are looking for them. Early signs are:
- Sore mouth that hurts and does not heal within two weeks
- Thick, swollen, or rough spot on the lining of the mouth
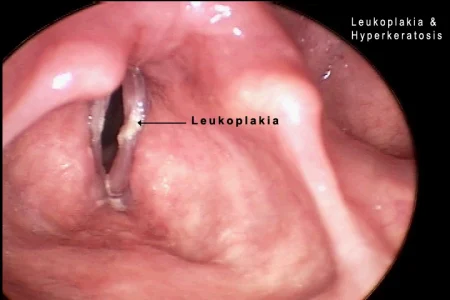
- Red areas, white areas, or speckled areas on tongue, on gum, or on lining of cheek
- Unexplained pain or tenderness, particularly painful eating or drinking
- Recurring or persistent pain or tenderness
They are simple to ignore, but if they persist for more than two weeks, you ought to visit a doctor or a dentist.
Symptoms of Advanced Oral Cancer
When oral cancer progresses and becomes serious, symptoms increase and multiply. They may be:
- Mouth, tongue, or throat continuous pain
- Painful chewing and swallowing food
- Loss of tongue or jaw function, or loss of the jaw
- Loose teeth without periodontal disease
- Mass or swollen lymph node in the neck
- Persistent foul breath
- Tinging of the tongue or other areas of the mouth
- Change in speech, slurred speech, or muffled speech
- Pain in the ear not due to ear infection
- Acute weight loss due to inability to consume food
Consult your doctor at once if you notice any of these signs and symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
There is no etiology of oral cancer. It is more an effect of a buildup of the risk factors. They are:
Tobacco Use
The most common etiologic agents for oral cancer are cigarettes, cigars, and pipes. Smokeless tobacco and snuff are even more so because they offer a vehicle for the mouth mucosa to come into contact for a longer time.
Alcohol Use
Chronic alcohol use is also a cause of etiologic mouth cancer, especially when it has been used in combination with tobacco.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Human Papillomavirus is a common human virus. It has been linked as a causative agent for certain mouth cancers. At the posterior of the throat and the back of the tongue.
Sun Exposure
Long exposure to the sun raises the risk of lip cancer.
Neglect of mouth care has been shown to cause long-term irritation and thus raise the risk for cancer.
Family History
Cancer of the mouth or a relative or even oneself raises oral cancer risk.
Age and Sex
Oral cancer is sure to develop in a person who is over 40 years of age. Oral cancer is more likely to develop in a male than a female.
Diagnosis of Oral Cancer
If the doctor or dentist suspects cancer of the mouth, then specific tests would be ordered to diagnose it.
Physical Exam
The doctor examines the lips, tongue, mouth, and throat for patches, soreness, or swelling.
Biopsy
The abnormal tissue is removed and examined with a microscope. It is the most sensitive diagnostic test for cancer.
Imaging Tests
X-ray, CT, MRI, or PET scan is performed to look for spread of cancer.
Endoscopy
A camera can be handed down through the mouth to more interior locations through a flexible tube.
Oral Cancer Stages

Like all cancers, oral cancer is staged:
- Stage 1: Tumor less than 2 cm without involved lymph nodes.
- Stage 2: Tumor 2–4 cm without involved lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: Large tumor or involved lymph nodes locally.
- Stage 4: Cancer spreads all over the body.
Staff stage is what physicians utilize to decide best what to do.
Treatment of Oral Cancer
The stage, site, and size of the cancer determine treatment. The treatment of choice is:
Surgery
Removal of the tumor along with a margin of tissue surrounding it.
If cancer has extended into an area beyond the tumor, lymph nodes in the neck are also excised.
Radiation Therapy
High-energy beams kill the cancer cells.
Usually reserved after surgery or for cancers in an early stage of development.
Chemotherapy
Drugs are very effective at killing the cancer cells.
Used with radiation in advanced cancer.
Targeted Therapy
New drugs specifically target cancer cell growth.
Immunotherapy
Attributes the immune system to kill cancer cells, usually in advanced cancer.
Side Effects and Recovery
Savior treatment is not free. They can be:
- Pain and swelling after surgery
- Dry mouth and sore throat following radiation
- Nausea, tiredness, and hair loss after chemotherapy
- Dysarthria or swallowing difficulty following the therapy
Speech therapy, physical therapy, and diet rehabilitation might be needed.
Prevention of Oral Cancer
Prevention is the best oral cancer therapy. Follow these precautions:
- Avoid smoking and tobacco consumption.
- Consume alcohol in moderation.
- Protect the lips from the sun using a lip balm with sunscreen.
- Fruit and vegetables should be consumed in large quantities.
- Brush teeth every day and floss and have good oral hygiene.
- Regular check-up at the dentist.
- HPV vaccine.
When to Visit a Doctor
You should visit a dentist or physician if you experience:
- Sore that will not heal within two weeks
- White bump or red, sore thick patch in the mouth which will not heal and has not faded after two weeks
- Voice change or numbness
- Painful mouth or abnormally bleeding mouth
Early detection saves lives. Don’t wait until symptoms worsen.
FAQs
Is oral cancer common?
Yes. Oral cancer is the most common cancer globally.
Is oral cancer curable?
Yes. Oral cancer can be treated if caught early.
Is oral cancer for smokers only?
No. Although the highest risk factor is tobacco smoking, alcohol consumption, HPV, and sun exposure also lead to oral cancer.
How do I check myself for oral cancer at home?
Search for sores, bumps, or patches in your mouth and observe if they last more than two weeks. But that would have to be ruled out by a physician.
Survival rate of oral cancer?
Survival rate of oral cancer is good if one is diagnosed early but decreases if there is any such occurrence of cancer.
Mouth cancer is a killer disease that can be avoided. Its initial symptoms are benign and form one of a sore, lump, or patch in the mouth which comes and goes from time to time. If you are aware of these initial symptoms. Then consulting a doctor at the right time will save your life.
Healthy practices such as not smoking, moderate alcohol consumption, protection of your mouth from the sun, and brushing and flossing your teeth daily can reduce your risk. If something in your mouth is not going to leave. Then see a doctor or dentist.
Your smile, your voice, and being able to eat and speak are worth more than to be taken for granted. Your mouth hygiene today is safeguarding your future happiness and health.