Where our lives are in question, kidneys receive little attention because we care more about the heart, lungs, or brain. But your kidneys will be working to keep you alive and healthy. They remove waste products from your blood. They maintain your body’s fluid level in balance, and normalize your blood pressure. Something is wrong with them, and it can be terrible. Kidney cancer is the most lethal kidney disease.
Kidney cancer results when the cells of the kidney grow abnormally and uncontrollably. Kidney cancer at first will lack some of its symptoms, and therefore most of them do not know they have it until it is advanced. Its earliest symptoms are so important in receiving early treatment and increased prospects of healing.
What Is Kidney Cancer?
It is a kind of cancer that occurs in the kidneys. It usually starts in the small tubes in the kidneys called renal tubules. These are the tubes responsible for filtering blood and eliminating waste products. After cells in such tubes start growing abnormally, they start forming a mass or a tumor. There are tiny tumors that are benign while others become malignant and metastasize into the rest of the body.
The most common kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and causes about 90% of kidney cancer. Two others are uncommon kidney cancers that are more common in children, like transitional cell carcinoma and Wilms’ tumor.
Why Kidney Cancer Symptoms Are Difficult to Identify
Kidney cancer has also been referred to as a “silent disease” due to it having no apparent symptoms for some until very late. Everyone finds out by happenstance through a test for another issue. The cancer advances further down the line once symptoms actually arise.
This is partly the reason why, when you notice slight differences, it is important to heed your body. It is then that you are in the initial stages that the physicians have more treatment options and better survival.
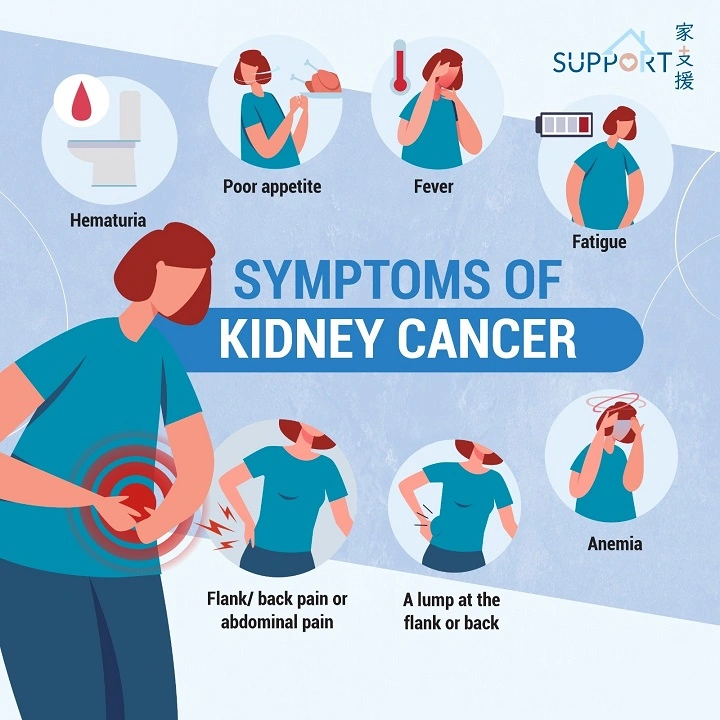
Symptoms of Kidney Cancer
There are certain common symptoms. You should watch out for those when you suspect it. Most cmmon symptoms are:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria): One of the initial and most common symptoms. The urine may be pink, red, or brown. Blood may be present but not even visible at times.
- Sore side or lower back pain: Pain is often below the ribcage and stabbing pain or a dull ache. It’s not the type that improves with rest, such as common back pain.
- Lump or swelling in the side or lower back: Your doctor can detect a lump if he presses inside your belly.
- Unexplained weight loss: Unexplained weight loss that is not due to dieting or exercise may be a symptom that weakness in the body has accumulated due to cancer.
- Weakness: Weakness in the body may be caused by cancer where one experiences much weakness after resting.
- Fever: There are individuals who might have recurrent fevers caused by non-infectious reasons.
- Loss of appetite: Sudden loss of appetite might imply something is amiss with your medical status.
Less Common Symptoms
In addition to the most common symptoms, others get:
- Swollen ankles and legs from buildup of fluid.
- Weakness and pallor from anemia (low red cell count).
- Night sweats and chills.
- Increased blood pressure from altered kidney function.
These are signs that you show due to these medical conditions too, but if they are transient for a long duration then it is always better to go and consult a doctor.
When to See a Doctor
Go and greet the doctor right away if you experience:
- Blood in urine, even a single time
- Occurring again and again pain in your side or back
- A bulge in lower back or belly
- Unexplained weight loss or extreme weakness
Don’t take it lightly. Even if it is not cancer, it is always wise to know why and treat it early.
Physician’s Approach in Diagnosing Kidney Cancer
When you visit a doctor with a symptom, he/she can examine the cause. These tests are:
- Blood tests: To determine the condition of the kidneys and find evidence of anemia.
- Urinary tests: To examine blood and other alterations.
- Imaging tests: Like ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to monitor the shape and size of kidneys.
- Biopsy: Small kidney tissue might be taken away sometimes to look for cancer cells.
Physicians can identify if there is cancer and how much it has grown.
Stages of Kidney Cancer
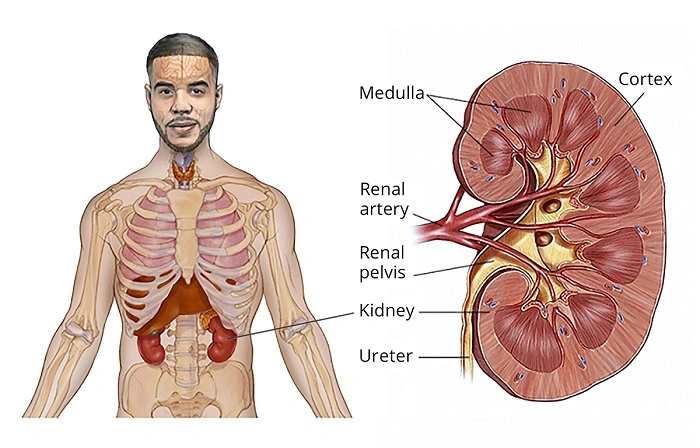
Physicians can easily decide what treatment to provide if they know the stage of kidney cancer.
- Stage 1: The cancer is small and within the kidney.
- Stage 2: The cancer is big but within the kidney.
- Stage 3: The cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or veins.
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to distant locations like lungs, bones, or liver.
The earlier it is detected, the greater the survival rate.
Also Read: Normal Bladder Volume by Age: A Guide
Treatment Options
Kidney cancer is treated based on the stage and overall condition of the patient. Some of the most used treatments include:
- Surgery: Half of kidney removal, also known as partial nephrectomy. Or entire kidney removal, also known as radical nephrectomy.
- Targeted therapy: Anti-cancer medication. It attacks the cancer cells and not normal cells.
- Immunotherapy: Anti-cancer medication that attacks cancer by enhancing the body’s immune system.
- Radiation therapy: Less often used but can be helpful if cancer is progressing and causes pain.
Doctors will work together to achieve maximum relief.
Kidney Cancer Symptoms – How to Manage Them
Kidney cancer is a bother, but the patient can manage symptoms if proper care is taken. Helpful tips are:
- Following a regular diet with sufficient fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.
- Intaking lots of water unless water intake is restricted by the doctor.
- Exercise regularly, for example, walking, to gain strength.
- Resting when exhausted and not overexerting oneself.
- Stress coping with counseling or support groups.
Prevention and Reducing Risk
You can’t always avoid kidney cancer. But you may decrease your risk by:
- Not smoking, which doubles the risk.
- Having a healthy weight.
- Managing hypertension with diet, exercise, or medication.
- Avoiding carcinogens over an extended period of time.
- Regular follow-up with your doctor in case you are genetically predisposed to kidney cancer.
These are steps that guarantee your health and well-being of your kidneys.
FAQs
Is kidney cancer ever diagnosed in the early stages?
Yes, occasionally when screening for other conditions. This is why one should attend check-ups occasionally.
Is kidney cancer always responsible for blood in urine?
No, because it may be caused by infection, kidney stones, etc. But always wound up nevertheless still.
Is kidney cancer treatable?
The majority, if they are discovered early enough, can be cured with surgery. Advanced ones are hard to cure but can be controlled in most cases.
Is pain associated with kidney cancer?
Yes, there is usually a side or lower back pain felt by the majority of the patients, especially in worse cases.
Who is most at risk?
Individuals aged 50 years and above, smokers, individuals with a history of high blood pressure. Also individuals with a history of kidney cancer in their families are more at risk.
Final Thoughts
Kidney cancer is a bad disease, but awareness of symptoms can save their lives. Hematuria, back pain, unexplained weight loss, and weakness are signs of some illness which should never be underestimated. If patients get early awareness of symptoms and meet physicians, they have much higher opportunities to receive proper treatment and live healthy lives.
Your kidneys are tiny. But they are capable of killing you. Look after them well, and monitor for warning signs. Don’t hesitate to go to your doctor if there is anything amiss.