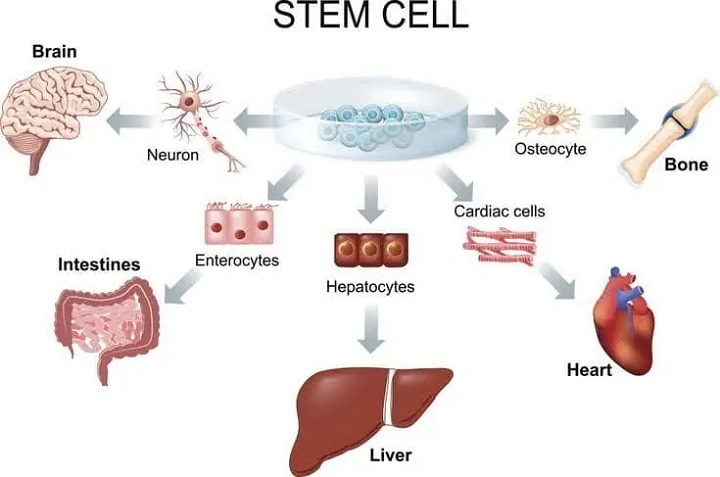
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a groundbreaking medical treatment with the potential to revolutionize healthcare. Stem cells possess unique properties that enable them to regenerate and repair damaged tissues in the body. Over the years, researchers have explored the therapeutic applications of stem cells in treating a wide range of diseases and medical conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the various diseases that can be treated using stem cell therapy.
Understanding Stem Cells:
Before diving into the specific diseases treated by stem cells, it’s essential to understand the basics of stem cell biology. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the remarkable ability to develop into different cell types in the body. They can self-renew, dividing and producing more stem cells, or differentiate into specialized cell types such as muscle cells, nerve cells, or blood cells.
Stem cells can be categorized into different types based on their origin and potency. These include embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Each type of stem cell offers unique advantages and potential applications in medical treatment.
List of Diseases Treated by Stem Cells:
- Orthopedic Conditions:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Degenerative disc disease
- Tendon and ligament injuries
Stem cell therapy holds promise in treating orthopedic conditions by promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from sources such as bone marrow or adipose tissue have shown efficacy in promoting cartilage repair and reducing pain associated with osteoarthritis.
- Neurological Disorders:
- Parkinson’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Spinal cord injury
- Stroke
Stem cell therapy offers potential benefits for patients with neurological disorders by replacing damaged neurons and promoting neural regeneration. Neural stem cells (NSCs) or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) can be used to generate neurons and support cells, offering hope for restoring lost function and improving quality of life.
- Cardiovascular Diseases:
- Heart failure
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Peripheral artery disease
Stem cell-based approaches aim to repair damaged heart tissue and improve cardiac function in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) or cardiac progenitor cells can be delivered directly to the heart tissue to promote angiogenesis, reduce scar formation, and enhance cardiac regeneration.
- Autoimmune Disorders:
- Multiple sclerosis
- Type 1 diabetes
- Lupus
- Crohn’s disease
Stem cell therapy holds potential in modulating immune responses and suppressing aberrant immune reactions observed in autoimmune disorders. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been explored as a treatment option to reset the immune system and induce tolerance, offering hope for long-term remission in autoimmune diseases.
- Hematological Disorders:
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Sickle cell anemia
- Thalassemia
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) remains a cornerstone in the treatment of various hematological disorders. Stem cells derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood can be transplanted to replenish the patient’s blood and immune system, providing a potential cure for conditions such as leukemia and lymphoma.
- Genetic Disorders:
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Cystic fibrosis
- Huntington’s disease
- Down syndrome
Stem cell therapy holds promise in treating genetic disorders by replacing or repairing defective cells with healthy functional cells. Gene editing techniques combined with stem cell transplantation offer potential avenues for correcting genetic mutations and alleviating symptoms associated with inherited diseases.
- Liver Diseases:
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatitis
- Liver failure
Liver stem cell transplantation or hepatocyte transplantation holds potential in treating liver diseases by replacing damaged hepatocytes and promoting liver regeneration. Stem cells derived from sources such as the bone marrow or liver tissue can be used to restore liver function and improve patient outcomes.
- Eye Disorders:
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Corneal disorders
Stem cell-based therapies offer potential treatments for various eye disorders by replacing damaged retinal cells and restoring visual function. Retinal pigment epithelial cells derived from pluripotent stem cells or adult stem cells can be transplanted into the retina to replace dysfunctional cells and preserve vision.
Stem cell therapy holds immense promise in revolutionizing the treatment of a wide range of diseases and medical conditions. From orthopedic disorders to neurological diseases, cardiovascular conditions, and genetic disorders, stem cells offer potential avenues for tissue regeneration, repair, and disease modification. While much progress has been made in the field of stem cell research, continued advancements and clinical trials are essential to harness the full potential of stem cell therapy in improving patient outcomes and quality of life. As research progresses, we can expect to see further breakthroughs in stem cell-based treatments, offering hope for patients with currently incurable diseases.