Our voice is among the most powerful tools of communication. We employ it on a daily basis to speak, sing, instruct, or express emotion. Voice disorders manifest in other people when they are evolving or as a result of some form of medical illness. Vocal cord atrophy is among them.
Vocal cord atrophy is thinning or weakening of vocal cord muscles. It is more difficult to speak with a clear, loud voice. The patients usually have a weak, breathy, or tremulous voice. Weakness of swallowing occurs in some of them.
This article will cover what vocal cord atrophy, why it occurs, how one can recognize the symptoms, how physicians diagnose it, what one can manage with, and how to control or avoid it better.
What Is Vocal Cord Atrophy?
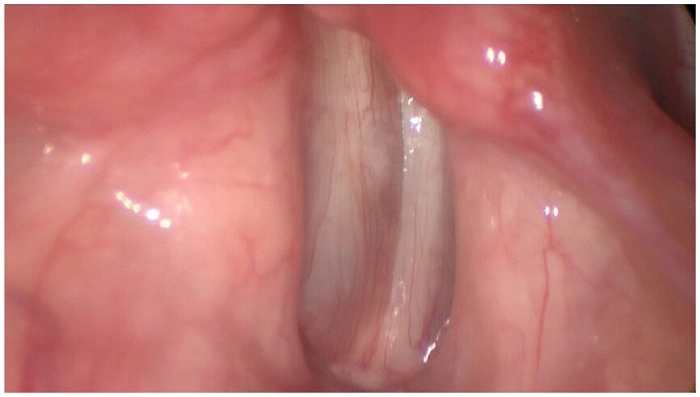
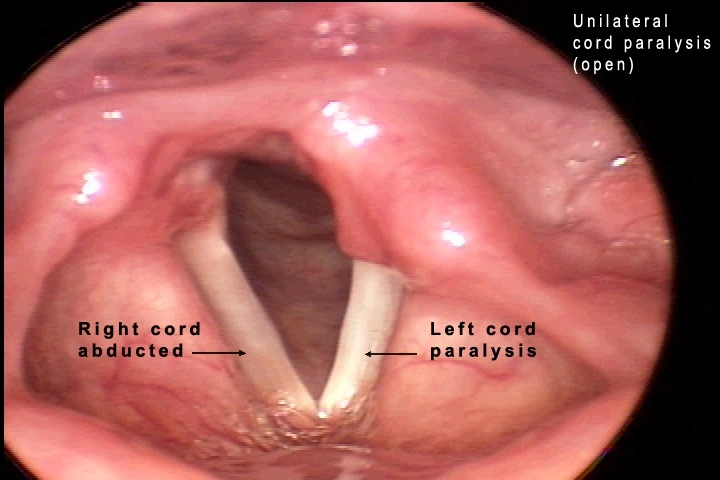
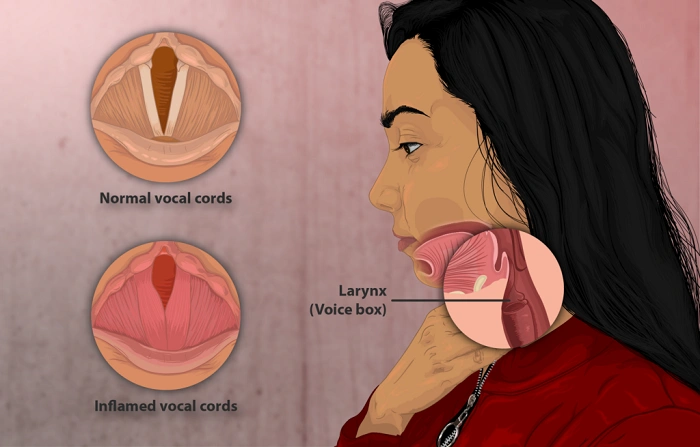
Vocal cords or vocal folds are two slender strands of muscle in the voice box or larynx. When air passes over them, they vibrate to create sound. Muscle strength and thickness help make the voice strong and stable.
In vocal cord atrophy, the muscles relax and get thinner. They lose their plumpness. Therefore, they cannot shut while one is speaking. So, the voice becomes weak, wheezy, and helpless.
It is also known as presbylaryngis at some points in time when it takes place as a result of aging.
Causes of Vocal Cord Atrophy
There are several causes because of which this disease can be developed. Some of the most popular causes include:
- Aging
As age grows, muscles start to lose their strength, and vocal cords are not an exception. It is an aging process that weakens the cords and makes them thinner.
- Nerve Issues
Trauma to nerves that innervate the vocal cords can cause weakness and atrophy. Parkinson’s disease or neurological disease is also a potential cause.
- Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance in older people can influence the voice strength of vocal cords.
- Chronic Conditions
Diabetes, thyroid disease, or autoimmune diseases can be the reason for weakening of vocal cords and muscles.
- Disuse
Like all other muscles in the body, vocal cords can weaken if they are not used as frequently. For example, people whose voice is not used a lot over many years are subjected to it.
- Surgery or Injury
Throat surgery, cancer radiation therapy, or trauma to the larynx can weaken or traumatize the vocal cords at times.
Symptoms of Vocal Cord Atrophy
These signs evolve with time and can vary with the level. The most common ones are:
- Weak or breathy voice
- Difficulty projecting the voice
- Fatiguing voice that tires during talking
- Shaky or shaky voice
- Difficulty hearing in noisy situations
- Trouble swallowing, often with food or liquid choking
- Frequent throat clearing
These signs and symptoms are threatening on a day-to-day basis. It first happens to singers, teachers, and speakers as they operate based on their voice.
How Vocal Cord Atrophy is Diagnosed
If one is having some trouble with his/her voice which will not go away after several weeks, he/she has to visit an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) doctor or a laryngologist. The doctor can perform the following:
- Medical Question and History
The doctor will ask for symptoms, habits, and medical history.
- Voice Assessment
Speech therapists will examine how the voice is working, pitch, loudness, and quality.
- Laryngoscopy
A flexible, long tube with light at one end is inserted through the throat to examine the vocal cords. This determines whether they are thin, weak, or failing to close.
- Stroboscopy
There is a unique lamp utilized for finding the vibration of vocal cords in colored lights. It assures doctors of the diagnosis.
Treatment of Vocal Cord Atrophy
Fortunately, vocal cord atrophy may be treated by some treatments. The choice relies on how severe the issue is.
Voice Therapy
Voice therapy is the first treatment most often. The patient is directed by a speech-language pathologist through some exercises in order to assist the voice and allow breathing. These can be:
- Breathing exercises to keep the air
- Soft voice exercises to strengthen the vocal cords
- Posture and relaxation exercises for increased control of the voice
Treatment is usually the exercise done on a daily basis for weeks or months.
Medications
In certain instances, medication is administered if the disease of atrophy is caused by another factor. For instance, thyroid medication or hormone medication can be helpful in case the same is the situation.
Vocal Cord Injection
Physicians inject certain fillers inside the vocal cords so that they get thicker. The fillers cause the cords to close tighter during speech. The procedure is usually easy and carried out under local anesthesia.
Surgery (Thyroplasty)
If injection or treatment does not work, surgery is advised. During thyroplasty, an implant is put in the larynx and it pushes the vocal cord into the middle and the voice becomes louder.
Lifestyle Changes
- Stop smoking and drinking as they make the vocal cords sore.
- Have water in small amounts regularly to moisten the throat.
- Speak into a microphone while talking in large halls or in public as straining is prevented.
Living With Vocal Cord Atrophy
It can be fatiguing to live with this, particularly if voice matters at the workplace. However, with proper care and treatment, most of the patients can handle it without any issues. The patients are usually asked to alter some habits:
- Speak slowly and articulately to avoid fatiguing the voice.
- Take breaks when speaking for extended durations.
- Use voice amplifiers in class or during large gatherings.
- Do exercises using the voice regularly.
Relations and friends also have to show support, as soft voice sometimes turns into social withdrawal.
Prevention of Vocal Cord Atrophy
It cannot be prevented in every case, especially the one due to self-age. There are some measures, though, through which voice might be kept healthy and strong for a longer duration:
- Drink sufficient water, 6-8 glasses daily.
- Control exercises against smoking and smoking by others.
- Control caffeine and alcohol intake as they dehydrate the throat.
- Practice good technique while doing loud talking or singing.
- Avoid voice overuse by screaming.
- Maintain muscle power by maintaining a good diet.
- Keep the general body muscles by exercise.
Cost of Treatment
Cost of vocal cord atrophy treatment depends upon the type of treatment:
- Voice therapy session: $50-$150 per session
- Injections: $500-$2,000 based on the content of the injections
- Surgery (thyroplasty): $5,000-$15,000
- Doctor consultation and tests: $200-$500
Some of the cost can be funded through insurance. It can be done especially if the condition affects health and activities of daily living. Cosmetic change in voice will not be as often reimbursed.
FAQs
Is vocal cord atrophy treatable?
It can’t always be reversed. But symptoms may be eased through treatment, injections, or surgery.
Does vocal cord atrophy occur solely in older individuals?
No. It does happen more in older people. But it can happen to young people because of nerve damage, surgery, or other reasons.
Is it dangerous?
It is not life-threatening, although it does paralyze quality of life. It also brings about swallowing difficulty in some patients.
How long is the recovery with treatment?
Voice therapy can improve in weeks’ time. While injections or surgical interventions repair the voice immediately but require follow-up.
Can singers with atrophy of the vocal cord still sing?
Yes, but perhaps with treatment, therapy, and voice care when attempting to sing safely.
Vocal cord atrophy is a condition in which the muscles of the vocal cords are thinned and weakened. Which causes a weak and breathy voice. It is common in older age. But it can also happen in young adults due to trauma, nerve damage, or disease.
With proper treatment, diagnosis, and suitable lifestyle adjustment, most of them improve. And symptoms can be managed. Voice therapy, injection, or surgery can work. Prevention by following good habits like sufficient intake of fluid, avoidance of smoking, and proper use of voice helps.
If you or the individual near you possesses a quivering or weak voice, don’t overlook it. Approach a doctor or a speech specialist. Early care will provide confidence-building, improved communication, and easy living.